Choose Services
Community Health
Racine Health Insights
Many factors contribute to citizens’ physical health in the City of Racine. Preventing the spread of communicableAble to be communicated to others. disease through vaccinations and other measures helps the citizens of Racine to be healthier and more productive. Understanding where improvements can be made allows for concentrating economic resources in areas that will deliver the greatest results for the community. This section contains information on demographics, chronic diseases, communicableAble to be communicated to others. diseases, sexually-transmitted infections, prevention, and other factors affecting health.
Demographic Information
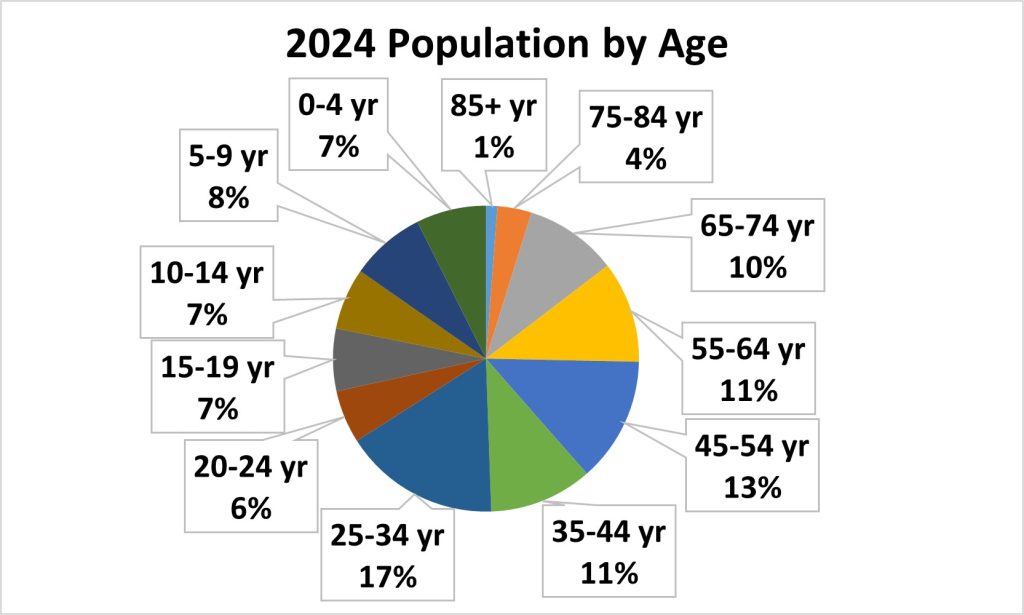
Age Distribution
The City of Racine shows a relatively balanced distribution across most age groups, with the 25–34 age group representing the largest segment of the population. In contrast, residents aged 85 and older make up the smallest proportion.
Source:
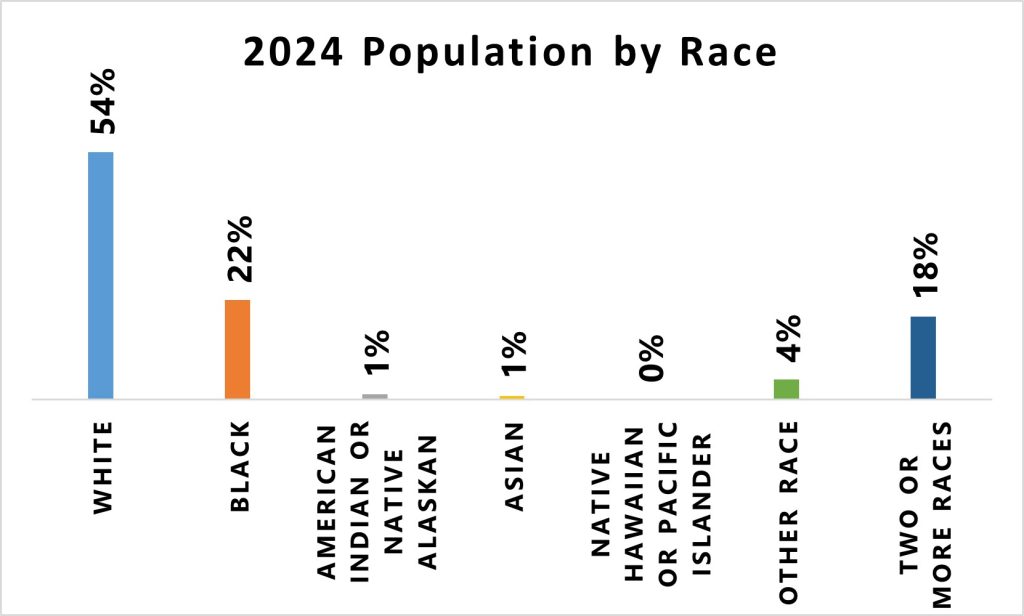
Race Distribution
The City of Racine has a highly diverse population, with White residents making up 54%, while Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander individuals represent less than 1%.
Source:
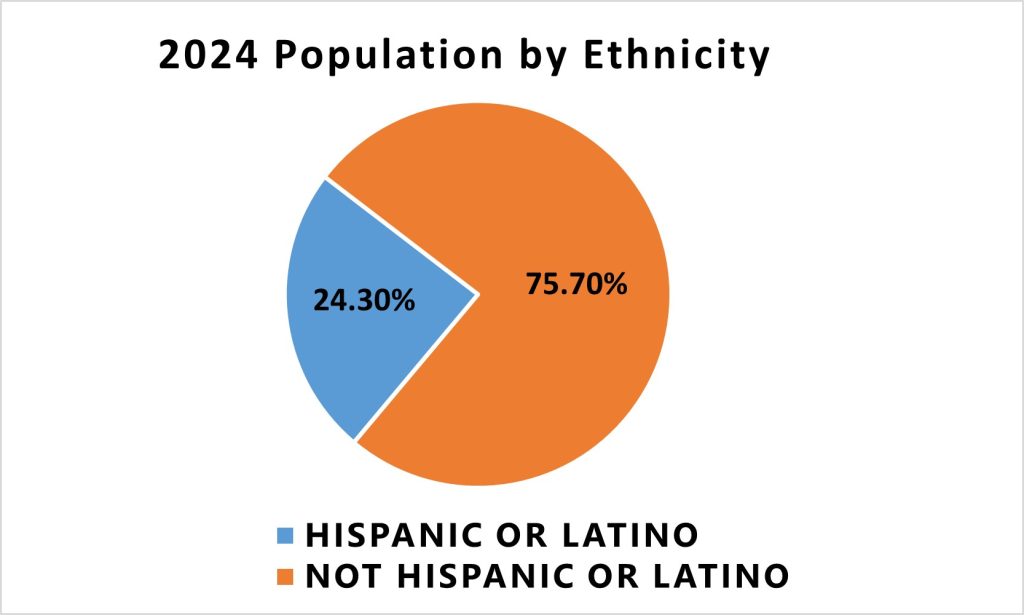
Ethnicity Distribution
Hispanics or Latinos make up approximately 24% of the City of Racine’s population, representing a significant portion of the community.
Source:
Obesity/Sedentary Lifestyle
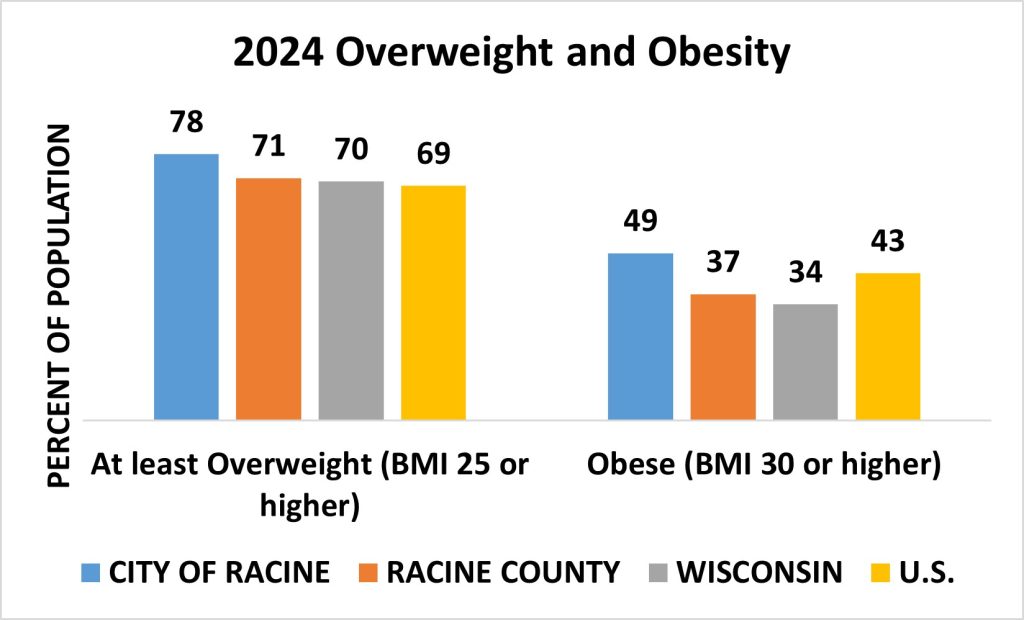
Obesity
The City of Racine has a higher percentage of overweight and obese individuals compared to Racine County, the state of Wisconsin, and the U.S. overall. However, the differences between these areas are relatively small.
Sources:
County Health Rankings & Roadmaps
Chronic Conditions
Chronic Health Conditions
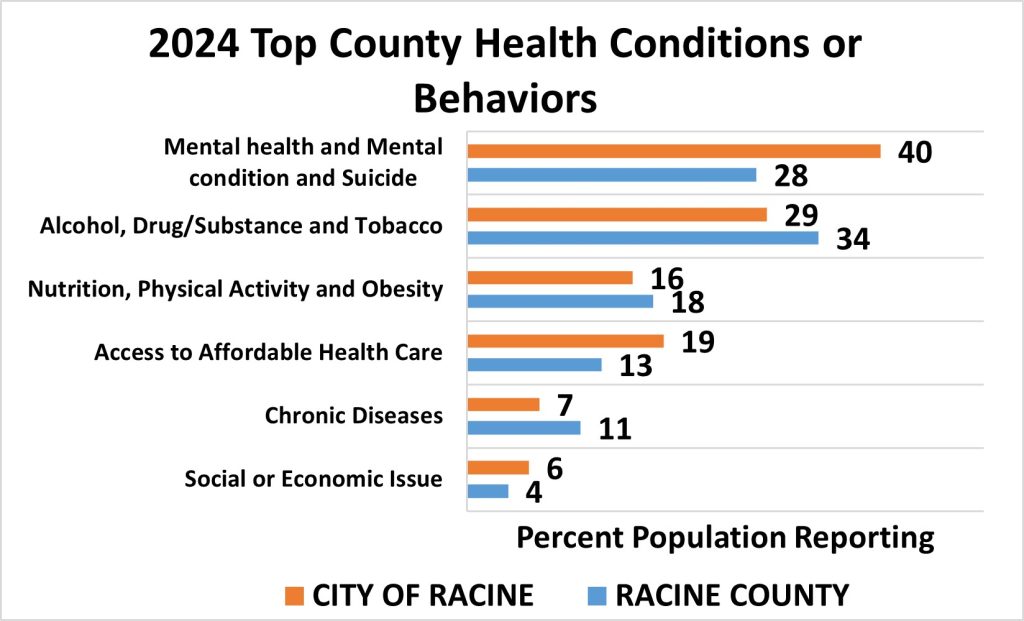
In 2024, several health conditions and behaviors were identified as priorities for intervention. Mental health, including mental health conditions and suicide, along with alcohol, drug/substance use, and tobacco, were among the top concerns highlighted by respondents from both the City of Racine and Racine County.
Source:
Preventative Procedures
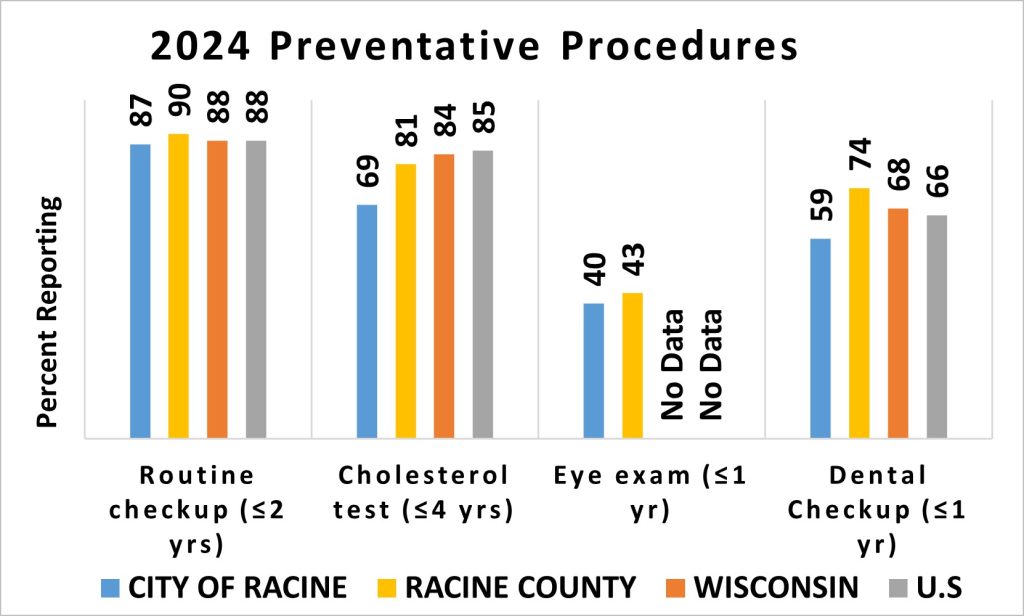
Preventive procedures play a vital role in maintaining overall health by detecting diseases in their early stages, leading to lower treatment costs and improved quality of life. When comparing residents of the City of Racine to those in Racine County, the State of Wisconsin, and the United States, similar trends are observed in adherenceAttachment or commitment to a person, cause, or belief. to recommended preventive care. However, the City of Racine shows notably greater disparities in cholesterol testing and dental check-ups compared to the other groups.
Source:
Leading Cause Of Death
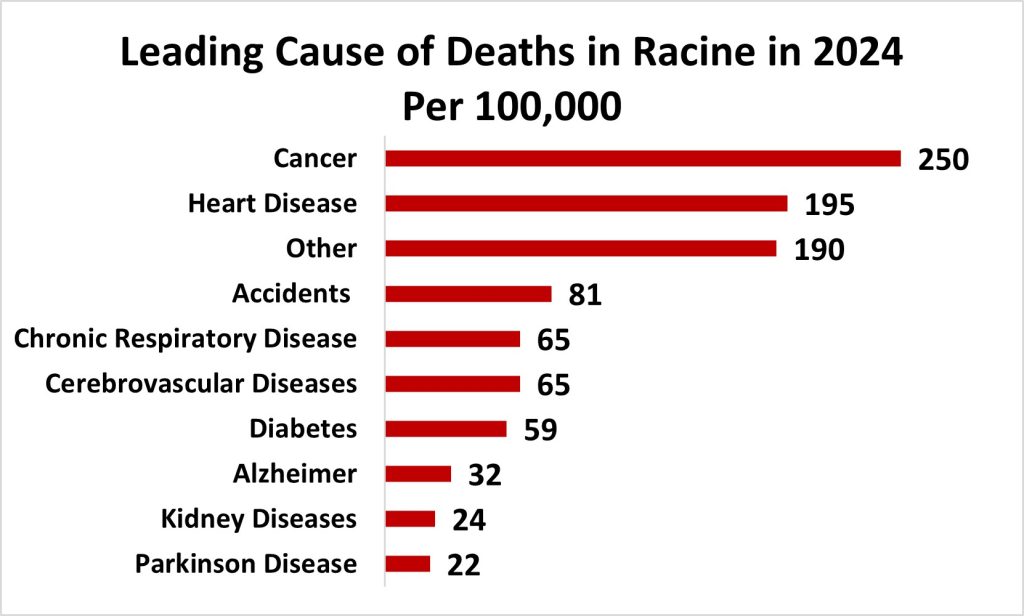
During 2024, heart disease and cancer are among the leading causes of death in Racine County. Not on the chart due to low and/or cause of death was not defined, “Other”, was a combination of not definitive and remainders of causes as death with a total count of 148 and a rate of 190 per 100,000.
Source:
Communicable Diseases
Diseases
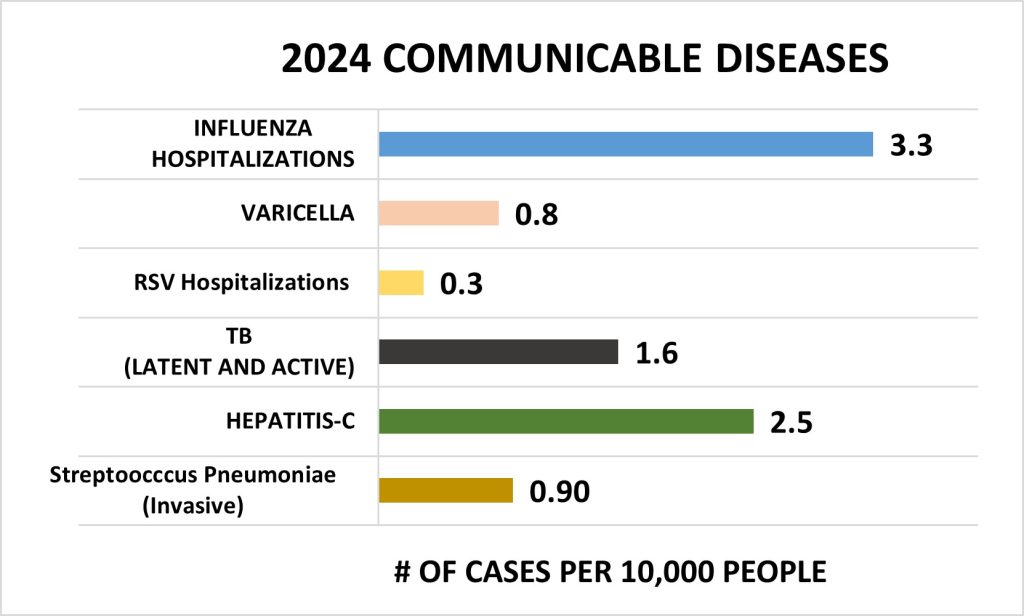
In 2024, influenza hospitalizations represented the most prevalent communicableAble to be communicated to others. disease in the City, with 3.3 cases per 10,000 residents. Hepatitis-C followed as the second most common, with 2.5 cases per 10,000, while RSV had one of the lowest rates, at just 0.3 cases per 10,000 residents.
Source:
City of Racine Public Health Department
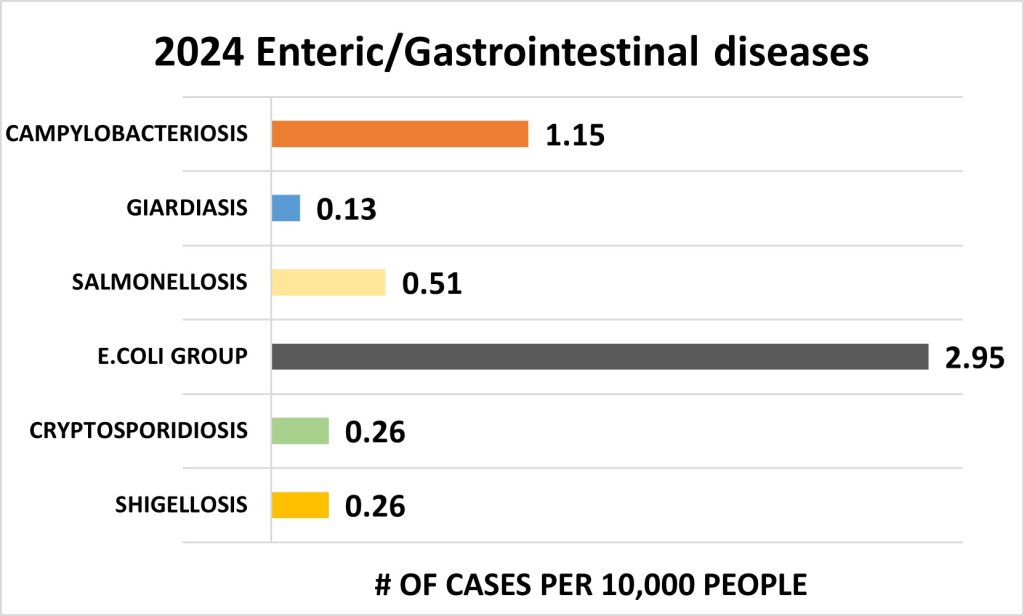
Enteric/Gastrointestinal Diseases
In 2024, E. coli infections comprising of Enteropathogenic (EPEC), Enterotoxigenic (ETEC), and Shiga toxin-producing (STEC) strains, accounted for the highest prevalence of enteric/gastrointestinal diseases in the City, with 2.95 cases per 10,000 residents.
Source:
City of Racine Public Health Department
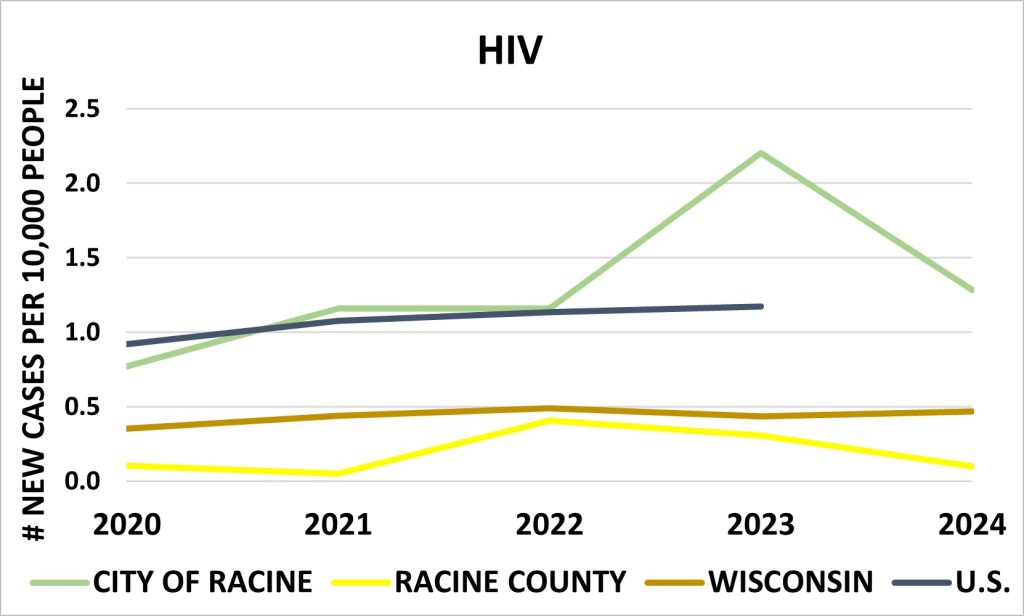
HIV
Since 2020, the rate of newly reported HIV cases in the City of Racine has increased. In 2023, the City reported a higher incidence rate than Racine County, the State of Wisconsin, and the United States. However, by 2024, both the City of Racine and Racine County experienced a decline in rates, while Wisconsin saw a slight increase
Sources:
City of Racine Public Health Department,
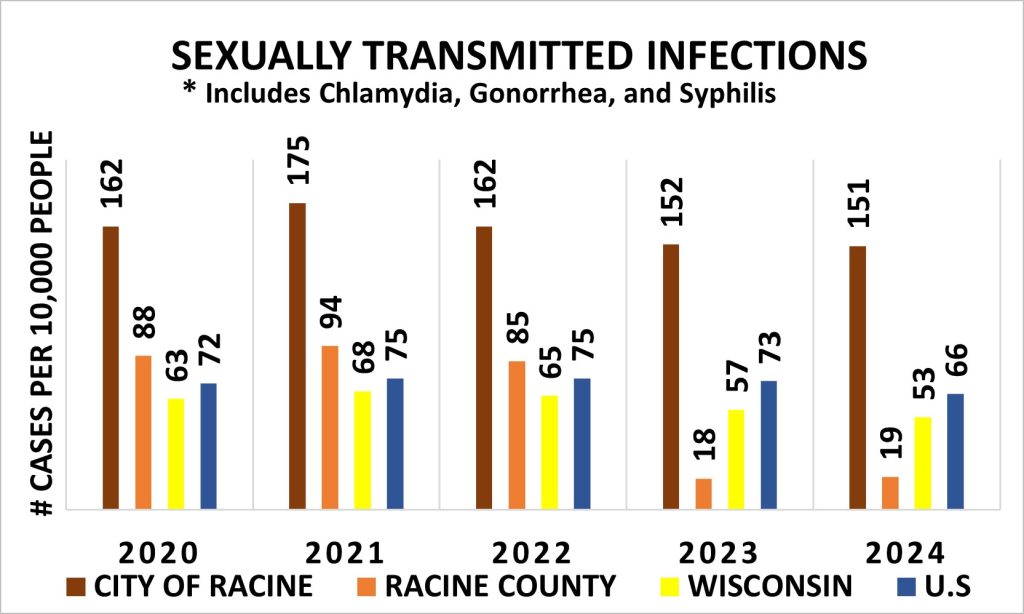
Sexually Transmitted Disease
The rate of sexually transmitted infections in the City of Racine has consistently remained much higher than the rest of Racine County, State of Wisconsin, and the United States throughout the years.
Sources:
City of Racine Public Health Department
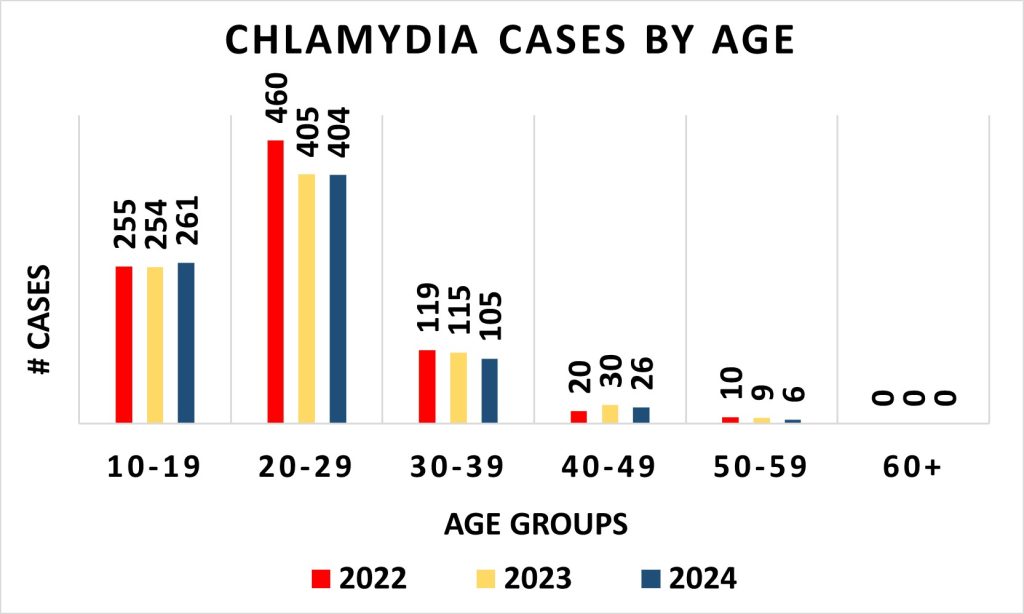
Chlamydia Cases By Age
The highest incidence of chlamydiaA common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis. consistently occur in persons 20-29 years old. While the number of cases has been fluctuating from year to year, the proportion of cases in each age group remains nearly the same for the City of Racine.
Source:
City of Racine Public Health Department
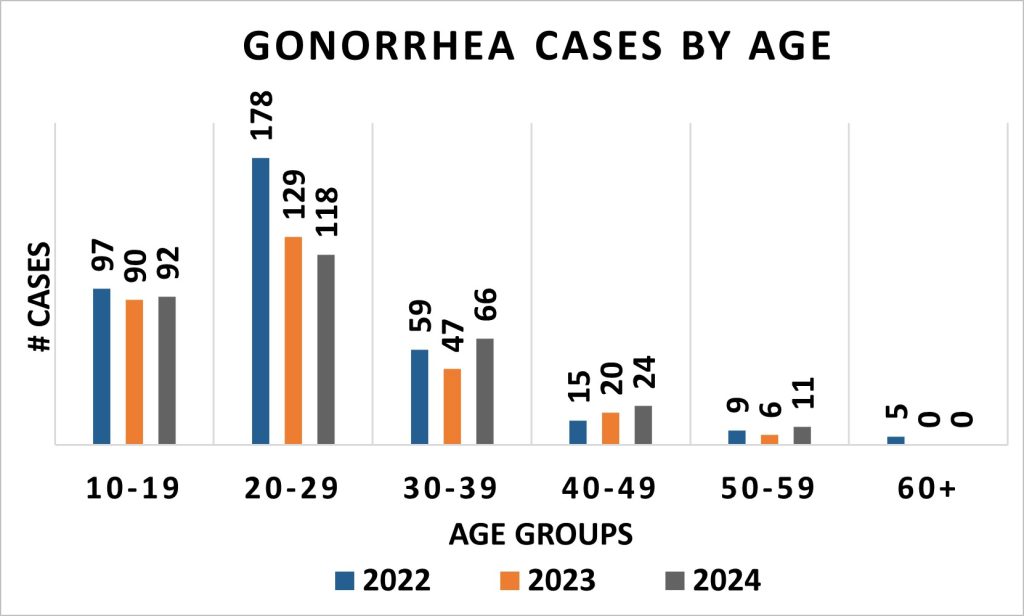
Gonorrhea Cases By Age
The group of 20-29 years old had the highest number of cases of gonorrheaA sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. From 2022 to 2024, there is a decrease in number of cases in each age group with the highest difference seen in 20-29 year old group in 2022 with 178 cases to 2024 with 118 cases.
Source:
City of Racine Public Health Department
Pertussis
Since 2020, pertussis (whooping cough) rates have steadily declined, with nearly no reported cases in the City of Racine and Racine County. However, in 2024, a significant increase in cases was observed across Wisconsin and the United States, with the State of Wisconsin experiencing the highest surge, reaching nearly 5 cases per 10,000 residents.
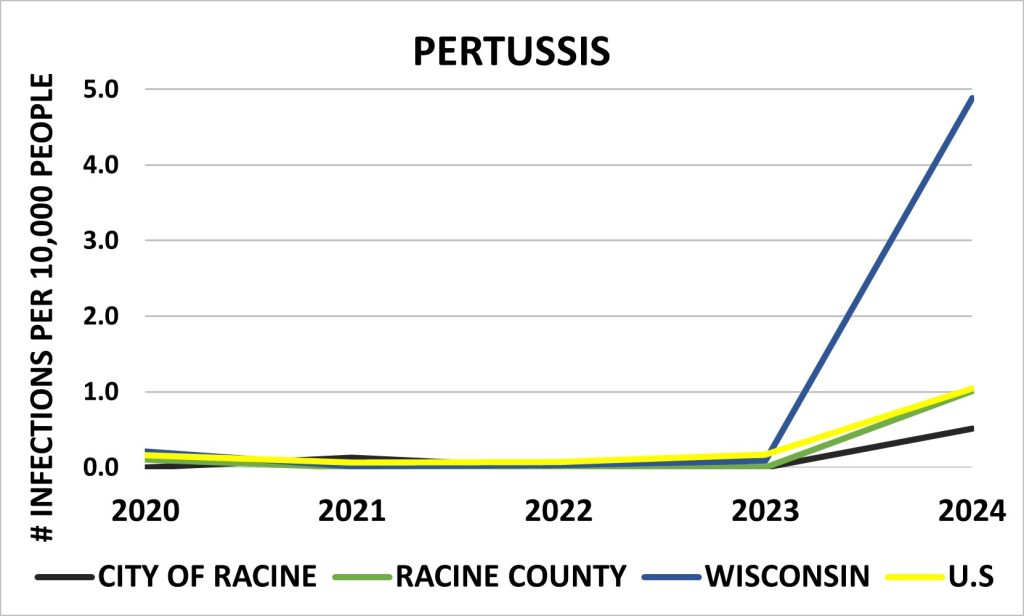
Sources:
City of Racine Public Health Department
Tuberculosis
While all geographic areas report low rates, the City of Racine and Racine County had the lowest rates in 2024, marking a decrease from 2023. In contrast, both the State of Wisconsin and the United States have shown a steady increase over the years.
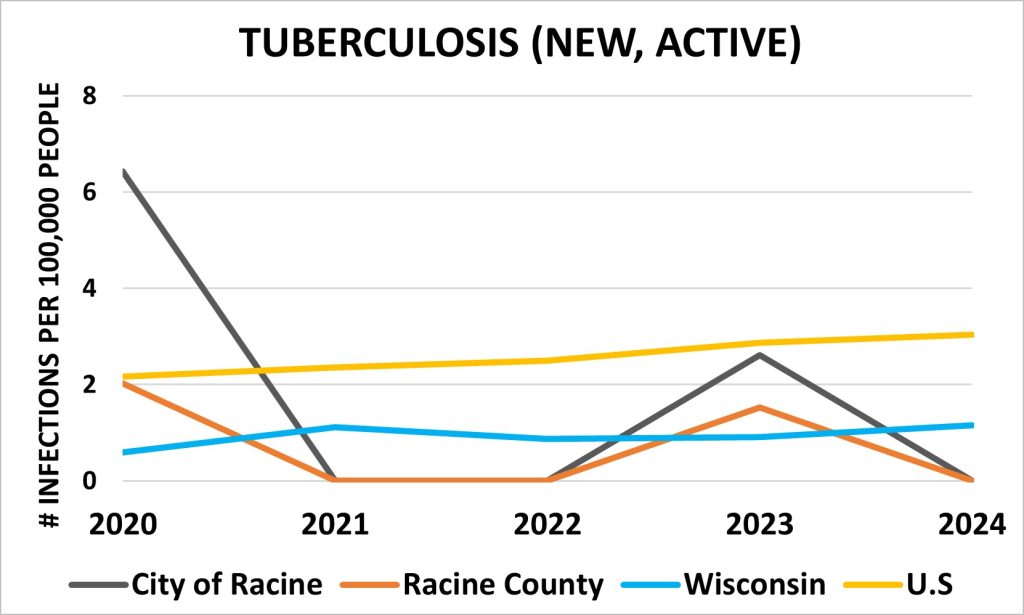
Sources:
City of Racine Public Health Department
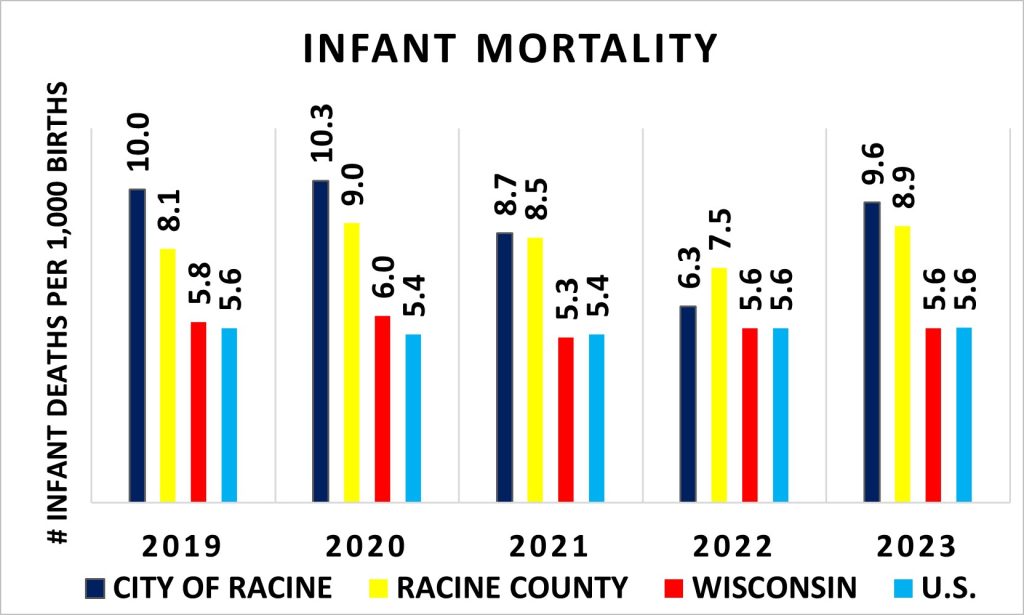
Infant Mortality
Mortality
The number of infant deaths in the City of Racine shows a consistent trend of remaining higher than the average infant mortality rate in Racine County, the State of Wisconsin, and the U.S. In 2022, it was similar to it’s counterparts and even lower than Racine County but in 2024 increased to higher than the other counter parts.
Sources:
Women’s Health
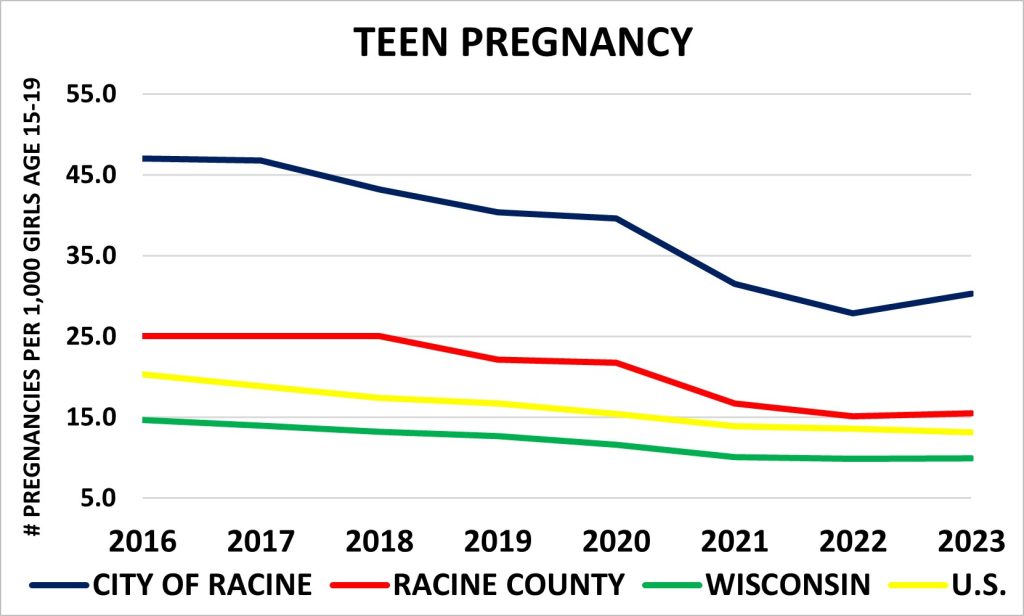
Teen Pregnancy
Teen pregnancy rate has fallen in the last few years for the City of Racine. It remains much higher than the rates for Racine County, the State of Wisconsin, and the U.S. Overall, teen-pregnancy rates have been decreasing in of the geographic locations. However, in 2023, the City of Racine showed an increased rate in comparison to previous year.
Source:
Children’s Health
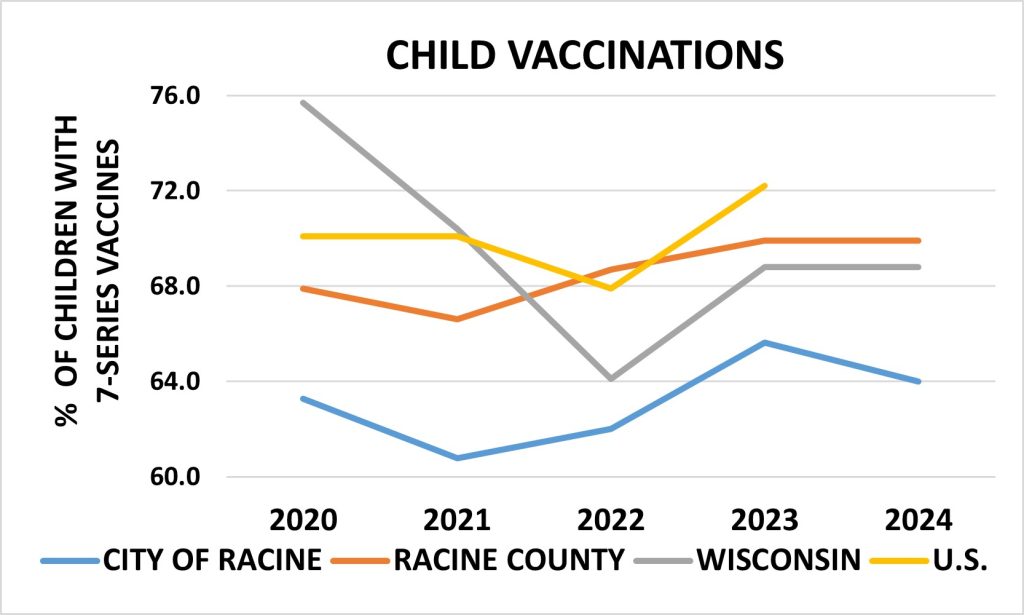
Child Vaccinations
The City of Racine has consistently reported lower completion rates for the 7-series vaccines compared to Racine County, Wisconsin, and the United States. However, in 2022, the City began to show an upward trend, with rates increasing in 2023, while rates in the other geographic areas remained stable.
Sources:
Violent Crime
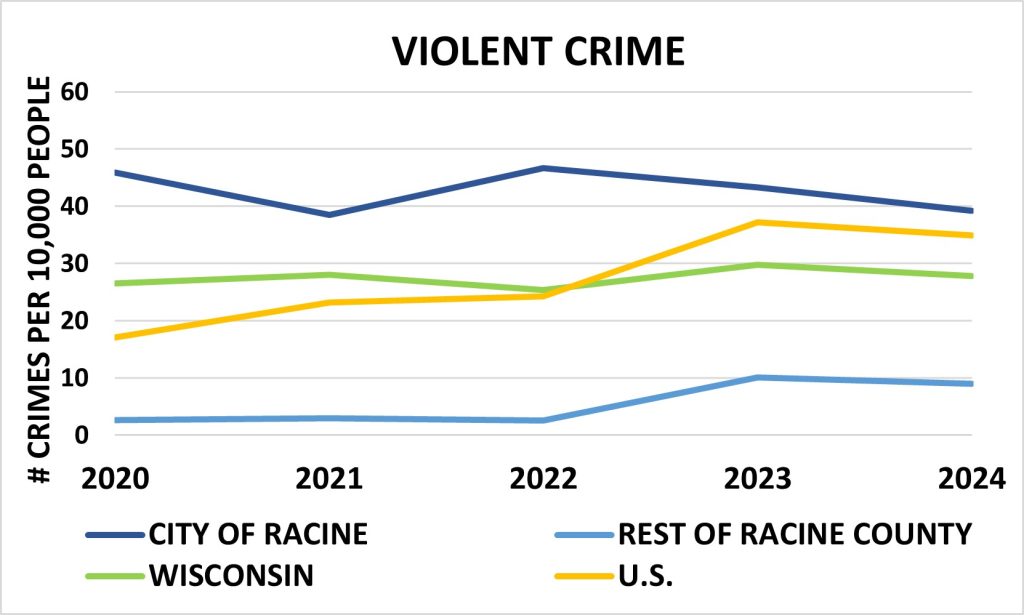
Rising Crime Rates
Violent crime is defined as murder, non-negligent manslaughter, forcible rape, robbery, and aggravated assault. The City of Racine has a higher rate of violent crimes than the rest of Racine County, the State of Wisconsin and the U.S. The rates for the state of Wisconsin, US and the rest of the county have remained steadily stable with the City of Racine increasing.
Source:
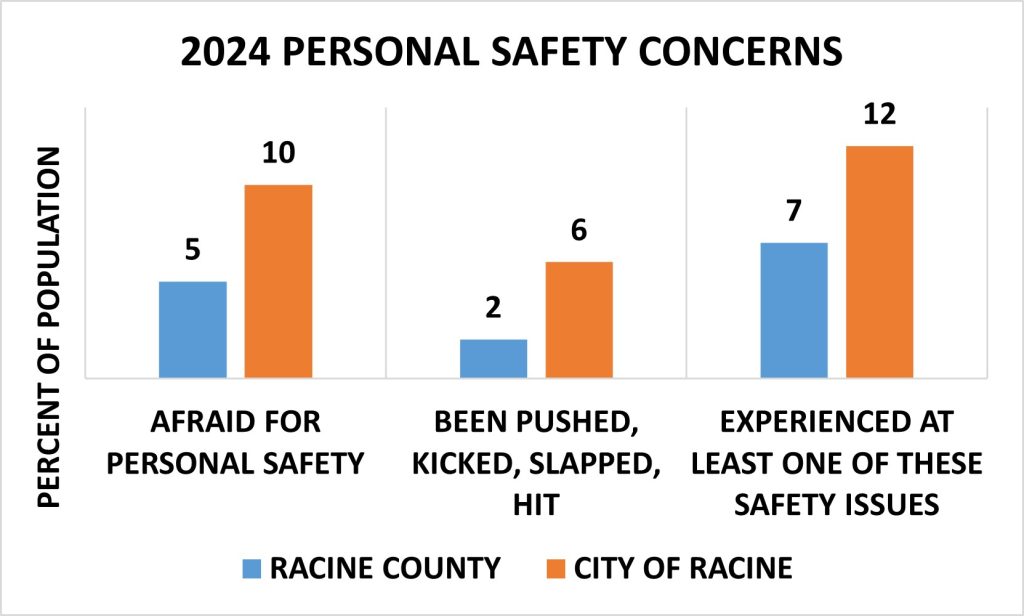
Personal Safety Concerns
In 2024, in both the County and City of Racine, five to twelve percent of residents reported having experienced at least one of the issues of been pushed, kicked, slapped or hit and/or afraid for their personal safety.
Source: